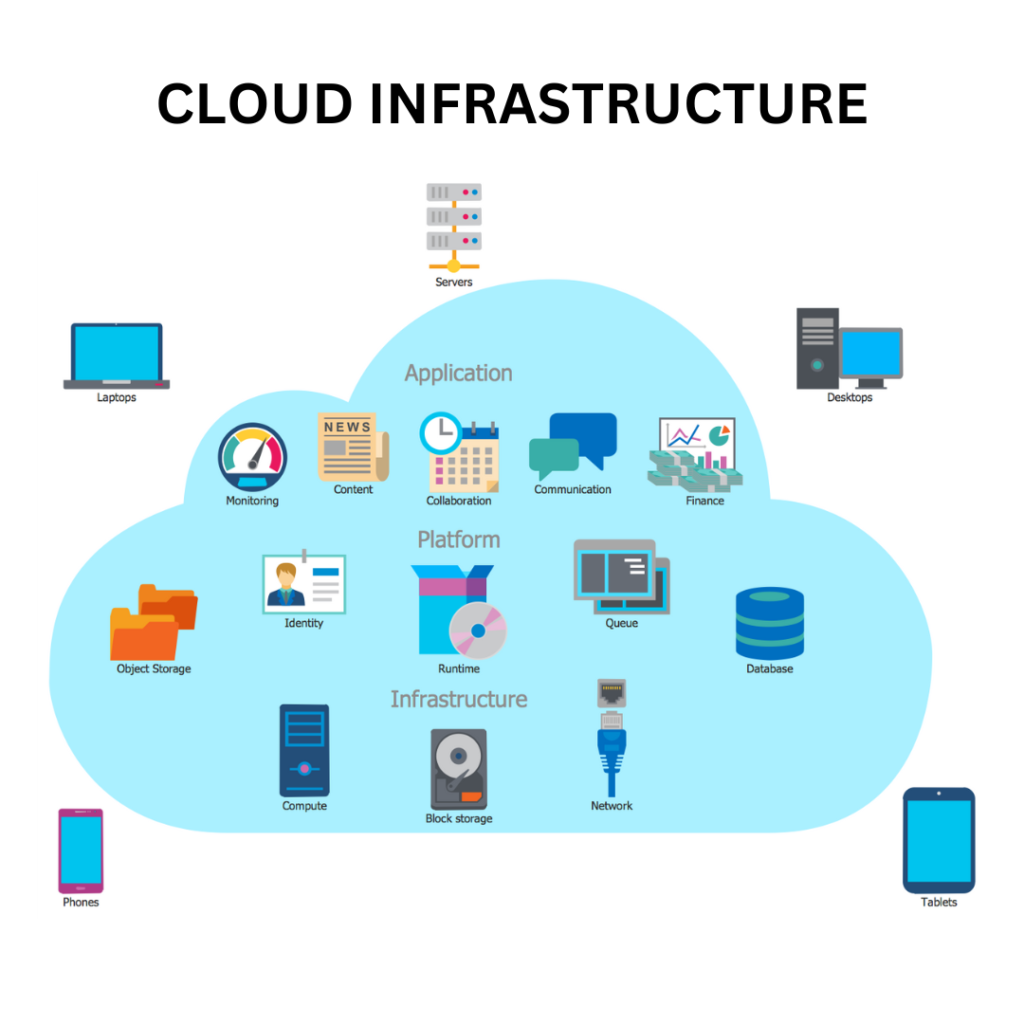
Cloud Computing – Transforming the IT Landscape
Cloud computing has swiftly emerged as a transformative force in the world of Information Technology (IT), revolutionizing the way businesses and individuals manage, store, and access data and applications. In this article, we will delve into the essence of cloud computing, decipher its significance in the modern IT landscape, and explore its fascinating journey from inception to its present-day dominance.
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Skills and Education for a Career in Cloud Computing
- Cloud Certifications as a Career Accelerator
- Educational Institutes in India and Abroad:
- Career Paths and Growth in Cloud Computing
- A Glimpse into the Professional Landscape
- Tips for Starting a Career in Cloud Computing
- Conclusion:
- FAQs
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing is a paradigm that involves delivering computing services over the internet. Instead of relying solely on local servers or personal computers to run applications and store data, cloud computing enables users to access these services via remote data centers, often operated by third-party providers.
The cloud model encompasses a wide range of services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, and more. In essence, it allows organizations and individuals to access on-demand computing resources without the need for extensive physical infrastructure.
Skills and Education for a Career in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is reshaping the technology landscape and is in high demand across the globe. To succeed in a career in cloud computing, it’s crucial to have the right mix of skills and qualifications. In this section, we will delve into the essential skills, qualifications, and the significance of certifications from leading cloud service providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Skills Required for a Career in Cloud Computing:
- Cloud Platform Proficiency: Familiarity with popular cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud is fundamental. Each platform has its own ecosystem, so a strong understanding of one or more of these is essential.
- Networking and Security: Knowledge of network protocols, security best practices, and understanding how to secure cloud environments is vital. Skills in configuring Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and implementing firewalls are often sought after.
- Scripting and Automation: Proficiency in scripting languages like Python and automation tools such as Ansible or Terraform is valuable for managing cloud resources efficiently.
- Containerization and Orchestration: Understanding containerization technologies like Docker and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes is becoming increasingly important as more companies adopt microservices architecture.
- Database Management: Competence in managing databases in the cloud, including SQL and NoSQL databases, is crucial for data-driven applications.
- DevOps Practices: Familiarity with DevOps methodologies and tools for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) is highly beneficial.
- Serverless Computing: Knowledge of serverless platforms, like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions, can be an added advantage in optimizing resource usage.
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Skills in monitoring cloud resources, analyzing logs, and diagnosing issues are important for ensuring the availability and performance of cloud-based applications.
- Soft Skills: Communication, problem-solving, and the ability to work well in teams are essential, as cloud computing often involves collaboration with various stakeholders.
Cloud Certifications as a Career Accelerator
Certifications from cloud service providers validate your expertise and can make you stand out in a competitive job market. The most well-known certifications are offered by AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
These certifications are not only recognized globally but also provide structured learning paths. Here are a few examples of certifications:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator
- Microsoft Azure:
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert
- Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert
- Google Cloud:
- Google Cloud Associate Cloud Engineer
- Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect
- Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer

Certifications are a testament to your knowledge and commitment to cloud technology, and many employers specifically look for certified professionals when hiring for cloud-related roles.
Educational Institutes in India and Abroad:
If you’re considering formal education in cloud computing, there are several renowned institutions in India and abroad that offer relevant programs and courses. Here are a few notable options:
In India:
- Indian Institute of Technology (IIT): Several IITs across India offer programs related to cloud computing and IT.
- National Institute of Information Technology (NIIT): NIIT offers cloud computing courses and certification programs.
- International Institute of Information Technology (IIIT): IIITs in India provide courses on cloud computing and related technologies.
Abroad:
- Stanford University, USA: Offers various courses in cloud computing and cloud-related specializations.
- University of Oxford, UK: Provides cloud computing courses and research opportunities.
- National University of Singapore: Offers a Master’s in Computing with a specialization in Cloud Computing.
Please note that you should research these institutions and their programs thoroughly to find the one that best fits your career goals and geographic preferences.
In conclusion, a career in cloud computing requires a strong foundation in cloud platform expertise, networking, scripting, and other technical skills. Additionally, certifications from top cloud service providers are invaluable for career advancement.
As cloud technology continues to evolve, staying updated with the latest skills and qualifications is essential for success in this dynamic field.
External Links:
https://aws.amazon.com/certification/
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/credentials/
https://cloud.google.com/learn/certification
Career Paths and Growth in Cloud Computing
A career in cloud computing offers a multitude of exciting opportunities for professionals at all stages of their careers.
In this section, we will explore the diverse career paths available, from entry-level positions to senior roles, and highlight the growth prospects, promotions, and salary increases that make this field so enticing.
Career Paths in Cloud Computing:
- Cloud Support and Operations:
- Entry-Level: Cloud Support Technicians provide essential support to cloud users, helping troubleshoot issues and ensuring system reliability.
- Growth: Progress to roles like Cloud Administrator, where you manage cloud resources and maintain system health.
- Cloud Development and Engineering:
- Entry-Level: Junior Cloud Developers assist in creating and maintaining cloud applications and services.
- Growth: Move into roles such as Cloud Engineer or Cloud Solutions Architect, designing and building complex cloud solutions.
- DevOps and Cloud Automation:
- Entry-Level: DevOps Interns assist in streamlining software development and deployment pipelines.
- Growth: Become a DevOps Engineer or Cloud DevOps Specialist, responsible for automating and optimizing processes.
- Cloud Security:
- Entry-Level: Junior Cloud Security Analysts assist in safeguarding cloud environments from threats.
- Growth: Progress to roles like Cloud Security Engineer or Cloud Security Architect, responsible for designing and implementing security measures.
- Data and Analytics in the Cloud:
- Entry-Level: Junior Data Analysts assist in managing and analyzing data stored in the cloud.
- Growth: Advance to roles like Data Engineer or Data Scientist, specializing in data analytics and machine learning.
- Cloud Sales and Solutions:
- Entry-Level: Sales Representatives promote cloud solutions and services to potential clients.
- Growth: Develop into roles like Cloud Sales Manager, responsible for leading sales teams and strategies.
- Cloud Project Management:
- Entry-Level: Project Coordinators help manage cloud projects and ensure they meet objectives.
- Growth: Evolve into Cloud Project Managers, overseeing complex projects and teams.
Growth Opportunities:
- Certifications: Earning certifications from cloud service providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) can significantly boost career prospects. Professionals with certifications are often more likely to be considered for promotions and specialized roles.
- Experience and Expertise: Gaining hands-on experience with different cloud technologies and services is essential for career growth. As you accumulate knowledge and expertise, you become eligible for more challenging and rewarding positions.
- Leadership Roles: With experience, cloud professionals can transition into leadership roles, such as Cloud Architect, Cloud Manager, or Chief Information Officer (CIO), where they oversee cloud strategies and lead teams.
- Salary Increases: The demand for cloud professionals often leads to competitive salaries. Entry-level positions in cloud computing are often well-paid, and salaries increase significantly with experience and expertise.
- Consulting and Entrepreneurship: Experienced cloud professionals may choose to become cloud consultants or start their own cloud-related businesses, offering specialized services and solutions to clients.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated with the latest trends and technologies in cloud computing is essential for career growth. Professionals who continue to learn and adapt to the evolving landscape are more likely to excel.

A Glimpse into the Professional Landscape
In the dynamic world of cloud computing, professionals take on diverse roles with unique day-to-day responsibilities. Whether you’re a Cloud Engineer, DevOps Specialist, or Cloud Security Analyst, each role is integral to the smooth operation and optimization of cloud services.
Let’s dive into the typical tasks and responsibilities of these professionals, providing insight into the inner workings of the cloud computing field.
1. Cloud Engineers:
- Provisioning and Configuration: Cloud Engineers focus on setting up and configuring cloud resources, ensuring that the infrastructure is optimized for performance.
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting: They continuously monitor the health of cloud environments, diagnosing and resolving issues as they arise.
- Automation: Cloud Engineers often use automation tools to streamline tasks like server provisioning and resource scaling.
2. DevOps Specialists:
- Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD): DevOps Specialists work on building and maintaining CI/CD pipelines, enabling the rapid and reliable release of software.
- Scripting and Automation: They write scripts and use automation tools to reduce manual tasks, enhancing efficiency.
- Collaboration: Collaboration is key as DevOps Specialists bridge the gap between development and IT operations teams.
3. Cloud Security Analysts:
- Security Monitoring: These professionals are responsible for monitoring cloud environments for security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response: In the event of a security incident, they investigate, contain, and remediate the issue.
- Policy Development: Cloud Security Analysts develop and enforce security policies to safeguard data and resources.
4. Data Engineers:
- Data Management: Data Engineers focus on data ingestion, transformation, and storage in the cloud, ensuring data is accessible and structured for analysis.
- ETL Processes: They create Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes to prepare data for analysis.
- Database Maintenance: Data Engineers maintain databases and ensure data integrity and availability.
5. Cloud Architects:
- Designing Solutions: Cloud Architects design and plan cloud solutions to meet specific business needs, selecting the appropriate cloud services.
- Cost Optimization: They consider cost-efficiency by selecting the right resources and scaling strategies.
- Capacity Planning: Cloud Architects plan for resource scalability and capacity management.
6. Cloud Sales and Solutions Professionals:
- Client Engagement: These professionals engage with clients, understanding their needs, and proposing cloud solutions.
- Solution Development: They design cloud solutions tailored to the client’s requirements.
- Sales and Negotiation: Part of the role involves sales and negotiation to secure contracts.
To learn more about other careers check out this website https://futurereadytools.com/category/careers/
7. Project Managers:
- Project Planning: Cloud Project Managers create project plans, defining tasks, timelines, and resources.
- Team Coordination: They oversee project teams, ensuring tasks are completed on schedule and within budget.
- Risk Management: Managing project risks, issues, and changes is also part of the role.
Tips for Starting a Career in Cloud Computing
The world of cloud computing offers an array of exciting opportunities, but getting started can be both thrilling and challenging. Whether you’re a recent graduate or looking to transition into this dynamic field, here are some practical tips to embark on a rewarding career in cloud computing.
1. Build a Strong Foundation:
- Begin by understanding the basics of cloud computing, including the key service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and deployment models (public, private, hybrid, multicloud).
- Explore the major cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to get a sense of the ecosystem.
2. Learn the Basics of Networking and Security:
- Networking is a fundamental skill in cloud computing. Understand concepts like Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), subnets, and firewalls.
- Get acquainted with cloud security best practices to protect data and resources.
3. Get Hands-On Experience:
- Sign up for free cloud service trials offered by AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to gain practical experience.
- Experiment with launching virtual machines, configuring databases, and deploying applications.
4. Learn Scripting and Automation:
- Python is a valuable scripting language in the cloud. Learn to write scripts to automate tasks and manage cloud resources.
- Explore automation tools like Ansible, Terraform, and Jenkins for infrastructure as code (IaC).
5. Embrace DevOps Practices:
- Familiarize yourself with DevOps principles, emphasizing collaboration, automation, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD).
- Study containerization technologies like Docker and orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
6. Pursue Relevant Certifications:
- Certifications from major cloud service providers are highly regarded. Start with entry-level certifications, like AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner or Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals.
- As you gain experience, consider more advanced certifications that match your career goals.
7. Online Learning Resources:
- Leverage online learning platforms such as Coursera, edX, Udemy, and Pluralsight to access cloud computing courses and tutorials.
- Many platforms offer specific courses for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
8. Community Engagement:
- Join cloud computing communities and forums. Platforms like Stack Overflow, GitHub, and Reddit have dedicated cloud computing sections where you can ask questions and learn from experts.
- Attend webinars, conferences, and meetups related to cloud computing to network with professionals in the field.
9. Set Up a Home Lab:
- Create a home lab to experiment with cloud technologies. You can use your lab to practice setting up servers, deploying applications, and troubleshooting issues.
10. Stay Updated:
Cloud computing is a rapidly evolving field. Subscribe to newsletters, follow cloud-related blogs, and participate in webinars to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and developments.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the journey through the cloud computing landscape has illuminated the profound impact of this technology on the IT and business world.
Cloud computing’s scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, as exemplified by IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS service models, have ushered in a new era of innovation and growth.
We’ve explored the pivotal role of certifications in empowering individuals to excel in a competitive job market and have delved into the diverse career paths within cloud computing, emphasizing the importance of continuous learning and experience for advancement.
The ever-increasing demand for cloud computing professionals underlines the urgency for businesses to transition to the cloud, making it a necessary choice for staying competitive.
As the engine behind innovation, scalability, and global connectivity, the cloud is driving businesses into the future.
If you’re considering a career in cloud computing, embrace it with confidence, knowing that your commitment to learning, certifications, and hands-on experience will be your guiding force toward success in this thriving field that shows no signs of slowing down.
FAQs
- What is cloud computing?
- Cloud computing is a technology that enables users to access and use computing resources (like servers, storage, databases, networking, software) over the internet, rather than owning and maintaining physical hardware or software.
- How does cloud computing work?
- Cloud computing works by providing on-demand access to a pool of configurable computing resources through the internet. Users can scale resources as needed and pay only for what they use.
- What are the benefits of cloud computing?
- Benefits include cost savings, scalability, flexibility, accessibility from anywhere, automatic updates, and improved collaboration. Cloud services also often provide robust security and reliability.
- Which companies provide cloud computing services?
- Major cloud service providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
- What are the different types of cloud computing models?
- The main models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Additionally, there’s Functions as a Service (FaaS) or serverless computing.
- How do I choose between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud?
- Consider factors like service offerings, pricing, geographic presence, and integration capabilities. Each platform has its strengths, so choose based on your specific requirements and preferences.
- What is serverless computing?
- Serverless computing, or Functions as a Service (FaaS), allows developers to run individual functions in response to events without managing the underlying infrastructure. It’s a pay-as-you-go model.
- What are the security concerns in cloud computing?
- Security concerns include data breaches, identity theft, insecure interfaces and APIs, and insufficient due diligence. Cloud providers implement security measures, but users must also follow best practices.
- How much does cloud computing cost?
- Cloud computing costs vary based on usage. Users pay for resources consumed, such as storage, compute power, and data transfer. Pricing models differ among cloud providers.
- What certifications are important for a career in cloud computing?
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate, and Google Cloud Certified – Professional Cloud Architect are popular certifications. The right certification depends on your chosen cloud platform and career path.