- Introduction
- The Role of a Project Manager
- Key Skills and Qualities of a Successful Project Manager
- Paths to become a Project Manager
- Navigating the Transition from a Different Career
- Job Opportunities in Project Management
- Project Management Jobs: Leading the Team to Success
- Skills and Qualities required for Project Manager
- Career Progression for Project Managers
- Advancing in Project Management: The Role of a Director
- Project Manager Positions in Various Industries
- Importance of PMP Certification
- Benefits of Obtaining PMP Certification
- Tips for Preparing and Passing the PMP Exam
- Project manager tools and resources
- Podcasts and Webinars
- FAQs
Introduction

In today’s rapidly changing business environment, Project Manager plays a crucial role in driving success for organizations across various industries. Skilled project managers serve as catalysts for transforming ideas into reality, be it bringing a product to the market, overseeing construction projects, or launching software development initiatives.
This comprehensive guide serves as a gateway to understanding the rewarding world of project management. We will delve into the responsibilities and essential skills of project managers, while also highlighting the distinctions between project managers and Project Management Professionals (PMPs). Moreover, we will explore pathways that can lead to a career in project management, such as gaining practical experience or transitioning from another profession.
However, our exploration doesn’t stop there. In an era marked by work and digital transformation, we will shed light on the realm of remote project manager positions. Additionally, we will examine roles in project management across diverse industries and discuss the unique challenges and opportunities faced by those working as project managers in the construction sector.
One essential pillar for building a career in project management is obtaining the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification. We will guide you through the importance of acquiring this recognized certification and how it can benefit your career. We will also provide advice on how to prepare for and excel in the PMP exam.
Obtaining the credential is just the beginning of your project management journey. We will show you how to advance in your career by focusing on education, building a network, and aspiring to leadership positions in project and program management.
In this article, we will equip you with a range of tools and resources for project managers, including project management software, professional associations, and online communities. Additionally, we will recommend books, blogs, and online courses that can help you stay up-to-date in this developing field.
Whether you are a project manager aiming for new heights or someone considering a career in project management for the first time, this article serves as a comprehensive guide to success. Let us embark on this journey together as we explore the opportunities that await you in the world of project management.
The Role of a Project Manager
Project managers are crucial for the execution of projects. Their responsibilities include ensuring projects are completed within the allocated time, and budget and with the desired level of quality. They have roles to play, such as guiding teams, managing resources effectively and delivering results. To pursue a career in this changing field, it is vital to understand the range of responsibilities and essential skills required by project managers.
Defining the Project Manager’s Responsibilities
A project manager plays a crucial role in the success of a project. Their responsibilities are diverse and encompass a wide range of tasks.
Project Planning
One of their primary tasks is project planning, which involves creating a detailed project plan that outlines the project objectives, scope, and deliverables. The project plan should be comprehensive and include timelines, milestones, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Resource allocation
Resource allocation is another essential responsibility of a project manager. They must assign tasks to team members, manage workloads, and ensure resource availability to meet project deadlines.
Risk Management
The project manager must also identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies to prevent them from derailing the project. Effective communication is a vital aspect of a project manager’s role. They must facilitate clear communication between team members, stakeholders, and clients to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Communication
Communication is key to keeping the project on track and ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly. Budget management is another core responsibility of a project manager.
Budgeting
They must manage project budgets, track expenses, and ensure that they deliver the project within the allocated budget. Quality assurance is also essential, and the project manager must monitor project deliverables to ensure they meet quality standards.
Timeline Management
Timeline management is critical to the success of a project. The project manager must track project timelines and milestones to ensure that the project is progressing as planned.
Issue Resolution
They must be proactive in addressing roadblocks and resolving issues as they arise to ensure that the project stays on track.
Stakeholder Management
The project manager must build and maintain strong relationships with project stakeholders to ensure that they are engaged and supportive throughout the project’s lifecycle. A project manager’s success depends on their ability to manage all these responsibilities effectively.
Key Skills and Qualities of a Successful Project Manager
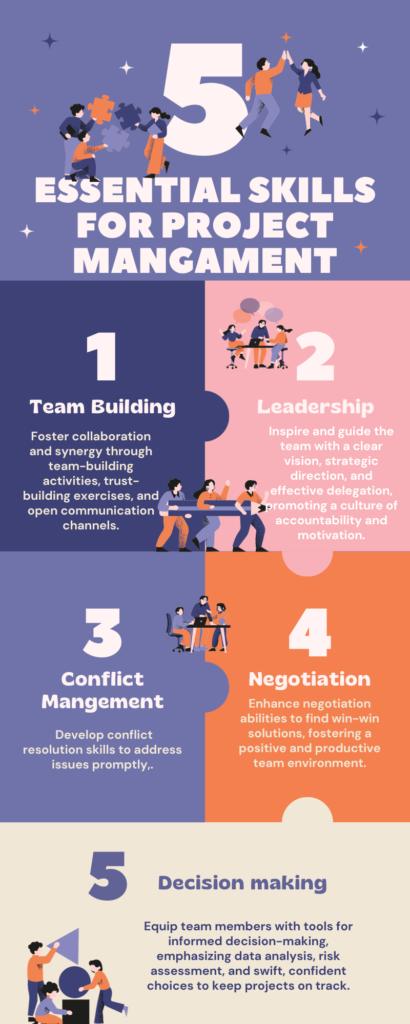
Becoming a successful project manager goes beyond understanding responsibilities it also requires specific skills and qualities. These include:
- Leadership: Inspiring and motivating team members to give their best.
- Effective Communication: Clearly conveying ideas, plans and progress to both the team members and stakeholders.
- Time Management: Ensuring that deadlines are met.
- Problem Solving: Being able to identify issues and come up with solutions.
- Adaptability: Being flexible in handling changing project requirements.
- Negotiation Skills: Having the ability to negotiate with team members, clients and vendors.
- Technical Proficiency: Understanding project management software and tools.
- Risk Management: Evaluating risks and taking steps to minimize them.
- Organizational Skills: Maintaining orderliness and structure within the project.
By possessing these skills and qualities you’ll be well equipped to be successful as a project manager.
Paths to become a Project Manager
Becoming a project manager can be an exciting and fulfilling career choice, but there are several paths that one can take to reach this goal. This section explores the different avenues that you can pursue on your journey to becoming a project manager, whether you’re starting from scratch or transitioning from another field.
Education and Certification required
One common path to becoming a project manager is through education and certification. Here’s how you can go about it:
- Bachelor’s Degree: Many project managers begin their journey by earning a bachelor’s degree in fields such as business administration, engineering, information technology, or a related discipline. This provides a solid foundation in project management principles.
- Master’s Degree: Pursuing a master’s degree in project management or a related field, such as an MBA with a concentration in project management, is an option for individuals looking to enhance their qualifications and career prospects.
- Project Management Certifications: Earning certifications such as the Project Management Professional (PMP) or Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) from reputable organizations like PMI is a common step. These certifications validate your knowledge and skills in project management.
Gaining Practical Experience
Practical experience is invaluable in the world of project management. Here’s how you can gain it:
- Entry-Level Positions: Starting in entry-level roles, like a project coordinator, project assistant, or junior project manager, allows you to learn the ropes and gain hands-on experience.
- Internships and Co-ops: Consider internships or co-op programs, especially if you’re a student or recent graduate. They provide exposure to real-world projects and mentors.
- Volunteer Work: Offering your project management skills on a volunteer basis for non-profit organizations or community projects is a great way to build your portfolio.
- Networking: Building a professional network by attending industry events, conferences, and joining project management associations can open doors to mentorship opportunities and job referrals.
Navigating the Transition from a Different Career
- If you’re looking to transition into project management from another career, it’s possible with a strategic approach:
- Transferable Skills: Identifying skills from your current career that are transferable to project management, like leadership, communication, and problem-solving that is valuable in both fields.
- Additional Training: Consider taking project management courses or pursuing certifications to fill any knowledge gaps. This demonstrates your commitment to the field.
- Tailored Resumes and Cover Letters: Customizing your resume and cover letter to highlight relevant skills and experiences that make you a strong candidate for project management roles, can increase your chances of getting hired.
- Informational Interviews: Connecting with current project managers for informational interviews can provide insight into their career paths and help seek advice on transitioning into the field. Each path has its own advantages and challenges, and the right one for you depends on your background, goals, and resources. Regardless of the path you choose, dedication and continuous learning are key to a successful project management career.
Job Opportunities in Project Management
Project Management: Exploring Diverse Career Paths
Project management is a versatile field that offers a wide range of job opportunities across various industries. In this section, we will explore the diverse career paths available to project managers, from remote project manager roles to positions in specific sectors like construction.
Remote Project Manager Jobs: Embracing the Digital Era
The digital age has transformed the way businesses operate, including how projects are managed. Overview of remote work: Remote work, a prominent trend, enables project managers to work from anywhere globally. This flexible approach to work has transformed the way professionals operate, offering project managers the freedom to manage projects from diverse locations.
Benefits and Challenges of Remote Work
Remote project management roles offer benefits such as enhanced flexibility and the elimination of commuting, providing professionals with the freedom to structure their workday as per their needs. However, these roles also pose challenges, such as potential communication barriers and the importance of maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Remote Project Management Tools:
Remote project managers rely on a range of essential tools and technologies to facilitate seamless collaboration with teams located across various regions. Here are some of the key tools that enable efficient communication, project tracking, and resource management.
Video Conferencing Platforms: Services like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet facilitate face-to-face virtual meetings and discussions.
Project Management Software: Applications like Trello, Asana, and Jira help in task assignment, tracking progress, and maintaining project timelines.
Cloud-Based File Sharing: Tools like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive allow for secure and accessible file sharing among team members.
Instant Messaging Apps: Platforms like Slack and Microsoft Teams offer real-time chat and file sharing for quick communication.
Virtual Whiteboards and Collaboration Boards: Miro and MURAL provide virtual spaces for brainstorming and visual collaboration.
Time Tracking and Productivity Tools: Applications like Toggl and RescueTime assist in monitoring work hours and productivity levels.
Team Communication and Document Collaboration: Tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams offer chat, document sharing, and collaboration features.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPN services ensure secure access to company networks and data from remote locations.
Video Recording and Screen Sharing: Software like Loom and ScreenFlow aid in creating instructional videos and sharing screens for demonstrations.
The Era of Remote work
- Transition to Remote Work During COVID-19: During the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations worldwide were compelled to adapt to the circumstances by allowing project managers and other employees to work from home.
- Trust and Transparency Established: Throughout the pandemic, many organizations developed a strong sense of trust and transparency with their remote workforce, as the need for effective communication and collaboration became paramount.
- Continuation of Remote Work Post-COVID: Owing to the success and trust cultivated during the COVID-19 period, remote work continued as a viable option even after the pandemic’s peak.
- Introduction of Hybrid Working Models: In response to the changing work landscape, organizations have introduced hybrid working models, which combine remote work and in-office work to cater to varying employee needs.
- Effective Remote Project Managers: Many project managers have demonstrated their effectiveness while working remotely, showcasing the adaptability and productivity of the role in a remote environment.
- Benefits of Remote Project Management: Remote project managers have excelled in delivering results, benefiting from reduced commuting time, enhanced work-life balance, and the ability to tap into a global talent pool.
- Flexible and Agile Workforce: Remote project managers contribute to creating a flexible and agile workforce that can quickly respond to changing project demands and collaborate effectively across geographical boundaries.
- Increased Job Satisfaction: The option of remote work has led to increased job satisfaction among project managers, as it allows for a more personalized and accommodating work environment.
- Enhanced Access to Talent: Remote work has opened up opportunities for organizations to tap into a broader talent pool, as they can hire skilled project managers from different regions and backgrounds.
- Sustainability Benefits: Remote work also aligns with sustainability efforts, as it reduces the carbon footprint associated with commuting and office infrastructure.
Project Management Jobs: Leading the Team to Success

Managerial roles, in project management come with responsibilities and opportunities for leadership. Here’s what you should know:
Role Overview: In project management managers have a range of tasks. They oversee projects and teams ensuring that the outcomes align with the goals of the organization.
Project Portfolio Management: Managers in project management are accountable for maintaining and prioritizing a portfolio of projects. They ensure that each project contributes to the objectives of the organization.
Team Leadership: These managers guide project teams, promoting collaboration and ensuring that team members are aligned with project goals, deadlines and deliverables.
Resource Allocation: Managers efficiently allocate resources such as personnel, budgets, and technology to optimize project execution.
Risk Mitigation: They identify risks that could impact the success of a project and develop strategies to minimize disruptions.
Stakeholder Engagement: Managers maintain relationships with stakeholders by keeping them informed and involved throughout the lifecycle of a project.
Quality Assurance: They oversee quality control measures to ensure that all project deliverables meet or exceed established standards.
Timely Decision Making: Managers make decisions promptly resolving any issues or obstacles that may arise during project execution.
Effective Reporting and Communication: Managers play a role in maintaining efficient communication channels ensuring that regular updates and reports are provided to stakeholders and senior management. This fosters a strong sense of collaboration. Keeps all parties informed.
Continuous Improvement for Enhanced Project Performance: A key responsibility of managers is to cultivate a culture of improvement. They regularly review project processes and outcomes actively seeking opportunities to enhance performance. By identifying areas for improvement managers ensure that projects evolve and adapt over time.
Alignment with Organizational Strategy: Managers diligently align project goals with the strategy. This ensures that projects are not efforts but instead contribute meaningfully to the long term success of the company. With this alignment projects become contributors to overall business objectives.
Evaluating Performance for Growth: Managers take on the task of assessing both project teams as an individual team members performances. Through feedback and coaching they support development within the team. This evaluation process promotes growth allowing individuals to continuously learn from their experiences.
The Crucial Role of Managers in Project Management: In summary managers in project management hold roles where they oversee projects manage teams efficiently handle resource allocation effectively mitigate risks proactively engage stakeholders consistently and align all efforts, with organizational objectives. Their expertise ensures project outcomes while fostering a work environment.
Skills and Qualities required for Project Manager
Project managers need to possess a combination of skills and qualities that empower them to excel in their multifaceted roles. These include;
- Thinking: Effective managers have the ability to think strategically seeing the picture and understanding how each individual project aligns, with the organizations overall goals and objectives.
- Decision Making: Managers must be decision makers, of making well informed and timely choices that keep projects on track and within their intended scope.
- Mentoring and Coaching: They should excel in mentoring and coaching team members helping them develop their skills and reach their potential.
- Leadership: Exceptional leadership is crucial as managers are responsible for guiding and inspiring project teams to achieve their work.
- Communication: Clear and concise communication is a skill, enablingthat managers to convey project objectives, progress and expectations to both team members and stakeholders.
- Time Management: Managers need strong time management skills to prioritize tasks meet deadlines and ensure progression of projects.
- Problem Solving: The ability to identify and efficiently solve problems is crucial as managers often encounter challenges during project execution.
- Adaptability: Given the nature of project management adaptability becomes key, for managers who must be flexible enough to adjust to changing circumstances and requirements.
Negotiation skills play a role, in dealing with team members, stakeholders and resource allocation. They aid managers in reaching agreements that benefit everyone involved. - Technical Proficiency:To be a successful project manager, it is crucial to possess technical proficiency in project management software and tools. This proficiency helps in effective project planning and monitoring of the project’s progress.
- Risk Management: As risk management is an essential aspect of project management, a project manager must have the ability to identify potential issues and develop mitigation strategies to minimize project disruptions.
- Organisational skills: Additionally, organizational skills are crucial for project managers to maintain a high level of organization, ensuring that project tasks, timelines, and resources are efficiently managed.
In summary successful project managers possess a diverse skill set and various qualities. These include thinking, decision making abilities, mentoring capabilities, leadership skills and effective communication techniques. These attributes enable them to navigate the complexities of project management and drive projects, towards outcomes.
Career Progression for Project Managers
Project management is a changing field that offers career paths each, with its own set of responsibilities and opportunities for growth. As project managers gain experience and expertise they have the chance to explore career avenues within the discipline;
- Project Manager: Project managers are tasked with planning, executing and closing individual projects. They oversee project teams handle budgets and ensure that projects are completed on time and within the defined scope. Aspiring project managers usually start their careers in entry level positions gradually gaining experience and skills before progressing to projects and greater responsibilities.
- Senior Project Manager: Senior project managers take on high impact projects. They often oversee project teams. Work closely with senior leadership to align projects with the organizations goals. Their extensive experience enables them to provide mentorship and guidance to project managers.
- Program Manager: Program managers are responsible for overseeing a portfolio of related projects and initiatives ensuring that they collectively contribute to objectives. They focus on the picture by managing interdependencies between projects and optimizing resource allocation across the program. Program managers play a role, in aligning project portfolios with an organizations vision.
Advancing in Project Management: The Role of a Director
In the realm of project management individuals can climb the ranks. Aspire to become a Director of Project Management or hold a position. This prestigious role entails overseeing a department or division dedicated to project management. In this article we will explore the responsibilities and importance of Directors in providing leadership and aligning projects, with long term objectives.
- Overseeing Departmental Operations:
As Directors of Project Management these professionals are entrusted with the task of supervising all aspects of their departments operations. They play a role in setting project management standards and ensuring that projects are executed efficiently. - Strategic Leadership:
Directors not oversee day to day operations but also provide leadership to their teams. They guide their department towards achieving long term objectives by aligning projects with the companys vision. Through planning and decision making Directors contribute to shaping the organizations project management culture. - Contributing to Executive Decision Making:
In addition to managing their department Directors may also participate in decision making processes. Their expertise and insights are valued when it comes to making choices that impact the organization as a whole. By providing input from a project management perspective they help shape business strategies.
The role of a Director of Project Management is integral in ensuring project execution within organizations. With responsibilities ranging from overseeing departments to contributing to decision making these professionals play a vital role in setting standards and aligning projects, with long term objectives. - To learn more about other careers check out this website https://futurereadytools.com/category/careers/
Project Manager Positions in Various Industries
Project management is not limited to one industry. It’s a skill set that can be applied across sectors. Let us take a look, at project manager roles in industries:
- Information Technology (IT): In the world of IT project managers play a role in overseeing the development and implementation of projects. They handle aspects of IT projects to ensure outcomes.
- Project Planning: When it comes to IT projects, meticulous planning is key. IT project managers carefully plan software, systems, or infrastructure projects by definingand objectives, scopes, and deliverables. They create project plans outlining the steps and resources for successful execution.
- Resource Allocation: These managers efficiently allocate resources like personnel, budgets, and technology to ensure that project teams have all the tools and support they need for their tasks.
- Team Leadership: Leadership is an aspect of their role as IT project managers lead functional teams comprising developers, engineers, analysts, and other IT professionals. They foster collaboration among team members while motivating them and maintaining a working environment.
- Risk Management: IT projects often come with challenges and potential risks. Skilled IT project managers excel at identifying these risks in the project lifecycle and developing effective strategies to mitigate them. This helps minimize disruptions, along the way.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring high quality is of importance, in IT projects. Managers play a role in overseeing quality control measures making sure that project deliverables meet or surpass established standards. They implement testing and validation processes to ensure the functionality of the software, integrity of systems, and reliability of infrastructure.
- Time Management: Meeting deadlines is vital in IT projects. Project managers diligently monitor project timelines and milestones. They take measures to keep the project on track and within schedule.
- Communication: Effective communication is an aspect of their role as they engage with stakeholders such as clients, end users, and senior management. Their goal is to provide updates gather feedback and ensure alignment with project goals and expectations.
- Technical Proficiency: Having proficiency in IT tools and technologies is essential for IT project managers. They possess an understanding of project management software, development platforms, and infrastructure solutions well as stay updated with emerging trends in the IT industry.
- Continuous improvement: Promoting a culture of improvement is another aspect they focus on. This involves fostering innovation within the team and identifying opportunities to enhance project processes for outcomes.
- In summary, IT project managers are drivers for software development projects or infrastructure initiatives within the information technology sector. Their comprehensive role covers planning, resource management, and leadership skills along, with risk mitigation techniques while emphasizing quality assurance through communication channels to achieve desired objectives.
Healthcare
Healthcare project managers play a role, in the evolving healthcare field. Their responsibilities encompass a range of functions aimed at enhancing patient care optimizing medical facilities and introducing cutting-edge healthcare technology solutions.
Improving healthcare: One of the areas where healthcare project managers make a significant impact is in improving care. They collaborate closely with healthcare providers, clinicians, and administrators to implement strategies and initiatives that enhance the quality of care provided to patients. This may involve streamlining processes reducing wait times and adopting patient-centered care models.
Managing medical facility :Another vital aspect of their role is overseeing medical facility projects. These projects are endeavors that demand planning and execution. Healthcare project managers ensure that healthcare facilities are designed, constructed, or renovated to meet the standards of safety, accessibility, and functionality. They manage budgets, schedules, and compliance with healthcare regulations to create spaces that facilitate the delivery of healthcare services.
In addition to facility management tasks healthcare project managers also play a role in implementing technology solutions within the industry. The use of technology has become pivotal for improving patient care and operational efficiency in healthcare settings. As leaders, in this area project managers oversee the implementation of health records (EHR) systems, telemedicine platforms, medical imaging solutions, and other innovative technologies. Their responsibility is not only to integrate these technologies into existing workflows but also to safeguard patient data privacy throughout the process.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance, with healthcare regulations and standards is extremely important. Healthcare project managers stay updated on changing regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) or the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). They make sure that healthcare projects follow these regulations to minimize financial risks.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaboration is an element of their role. Healthcare project managers work together with teams, including doctors, nurses, IT professionals, and facility management staff. Effective communication and teamwork are crucial in achieving project objectives and delivering high-quality healthcare services.
- Resource Allocation: Efficient resource management is vital in healthcare projects. Project managers allocate resources wisely from personnel to medical equipment and technology ensuring that healthcare facilities and services operate at their capacity.
- Emergency Preparedness: Healthcare project managers often play a role in emergency preparedness planning and response. They. Implement emergency protocols to guarantee care during crises, like natural disasters or public health emergencies.
- Finance: In the field of finance, project managers play a role, in overseeing a range of initiatives that are vital for the financial well-being and growth of organizations. They are responsible for managing projects related to mergers and acquisitions implementing software solutions and mitigating risks.
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): Finance project managers play a role in coordinating M&A activities. They lead teams from departments to navigate the process of integrating two or more companies. Their main focus is on ensuring transitions aligning systems and complying with regulatory requirements. The ultimate goal is to achieve synergy optimize cost structures and generate value for stakeholders.
- Financial Software Implementations: The implementation of financial software solutions is crucial for financial management. In this context finance project managers take charge of selecting software systems customizing them according to needs and successfully deploying them. They closely collaborate with IT teams to integrate accounting, payroll, budgeting, and reporting software seamlessly. This leads to processes improved data accuracy and enhanced capabilities for financial analysis.
- Risk Management Projects: Mitigating financial risks holds importance in the finance sector. Finance project managers bear the responsibility of identifying types of risks such, as market risk, credit risk, and operational risk. They further develop strategies to assess these risks effectively while working towards their mitigation.
- Risk analyst: They work together with risk analysts, compliance officers, and financial experts to implement frameworks for managing risks and ensuring adherence, to regulations.
- Budget Management: Managing budgets effectively is an aspect of their role. Finance project managers carefully. Monitor project budgets optimizing resource allocation to achieve goals.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Compliance with regulations is necessary in the finance sector. Finance project managers navigate the landscape of regulations making sure that projects comply with laws of the country they reside in. They establish protocols for compliance. Reporting to safeguard the integrity of finances.
- Stakeholder communication: Communication with stakeholders is vital. Finance project managers regularly interact with executives, board members, and investors providing them with updates on finances, valuable insights, and risk assessments.
- Continuous improvement: A culture of improvement is encouraged by finance project managers. They conduct evaluations after projects are completed to identify areas that can be optimized or where innovation can enhance processes.
- In summary project managers in finance play a role, in guiding initiatives that are crucial for maintaining financial stability and promoting growth.
The professionals, in this role have a range of responsibilities that are crucial for the financial success of organizations in the sector. They play a role in areas such, as mergers and acquisitions implementing software, managing risks, handling budgets ensuring regulatory compliance communicating with stakeholders, and constantly seeking ways to improve processes.
Marketing and Advertising
In the changing world of marketing and advertising project managers play a role, in overseeing and coordinating various important tasks. They are responsible for managing campaigns launching products and executing projects to ensure outcomes for marketing initiatives.
- Campaign Management: Project managers in the field of marketing are assigned to the planning, execution, and monitoring of marketing campaigns. They collaborate with teams such as designers, copywriters, and digital marketers to ensure that campaigns are delivered on time and within budget. Their primary focus is on achieving campaign goals whether it be increasing brand awareness generating leads or promoting products.
- Product Launches: Successful product launches are an aspect of marketing strategy. Marketing project managers take charge of orchestrating product launch activities starting from market research and positioning to go-to-market strategies. They meticulously. Execute all aspects of the product launch including messaging, pricing, and promotion to maximize impact in the market.
- Creative Projects: Marketing project managers also oversee aspects, like design, branding, and content creation that form a part of marketing endeavors.
- They work together with teams to bring marketing ideas to life. Their main focus is to ensure that branding guidelines are followed and that creative assets align, with the marketing strategy.
- Timeline Management: Managing timelines is crucial in marketing projects. Project managers carefully plan project timelines, set milestones, and monitor progress to make sure that marketing initiatives are executed according to schedule.
- Resource Management: Resource management plays a role in their responsibilities. Marketing project managers efficiently allocate resources, including resources and budgets to guarantee that marketing projects have the talent and support for success.
- Stakeholder communication: Effective communication is essential as they interact with stakeholders such as marketing directors, clients, and creative teams. They provide updates gather feedback and ensure that project deliverables are with marketing goals and expectations.
- Performance metrics: Evaluating the performance of marketing campaigns and projects is a part of their job. They implement analytics tools and reporting mechanisms to track performance indicators (KPIs) and assess the success of marketing initiatives.
- Continuous improvement: They foster a culture of improvement by conducting evaluations after each project. This helps identify areas for optimization and innovation, in both marketing strategies and processes.
To sum it up marketing project managers play a role in the success of marketing and advertising initiatives. They oversee aspects such, as campaign management, product launches, creative projects, timeline management, resource allocation, stakeholder communication, performance measurement, and continuous improvement. Their active involvement ensures that marketing strategies are effectively executed, and marketing goals are achieved.
Engineering and construction project manager
Project managers in the engineering and construction sectors play a crucial role in overseeing complex building and infrastructure projects. They face distinctive challenges and opportunities, requiring them to manage resources, budgets, timelines, quality, safety, stakeholder coordination, technology integration, contract management, and continuous improvement throughout projects.
In the construction industry, project managers encounter tight schedules, changing project scopes, and the need for precise cost estimation. They navigate regulatory requirements, environmental considerations, and safety standards while managing diverse teams and stakeholders.
Resource Allocation: Efficient resource allocation is pivotal, and project managers meticulously manage project budgets, monitoring expenses to ensure timely completion within financial constraints.
Time Management:Meeting project timelines is essential in construction, and project managers create comprehensive project schedules, set milestones, and actively track progress. They oversee quality control measures to ensure that structures meet engineering specifications and safety standards.
Compliance: Safety compliance is a top priority, and project managers enforce safety protocols, conduct risk assessments, and promote a culture of safety among project teams. Effective communication with stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and regulatory agencies, is crucial.
Stakeholder Communication: Project managers foster collaboration, address concerns, and keep stakeholders informed throughout the project lifecycle. They must also navigate environmental regulations and sustainability requirements, ensuring that construction projects adhere to eco-friendly practices and minimize environmental impact.
Technology Integration: Embracing technology is essential for efficiency, and project managers leverage construction management software, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and other tools to streamline project workflows and enhance communication.
Contract Management: Construction projects often involve multiple contracts and subcontractors, and project managers manage contracts, negotiate terms, and ensure that all parties fulfill their obligations.
Continuous improvement: Promoting continuous improvement, project managers conduct post-project evaluations, identify areas for optimization, and implement best practices in construction processes.
Overall, project managers in the engineering and construction sectors play a pivotal role in overcoming unique challenges while capitalizing on opportunities, ensuring the successful execution of complex construction projects.
Importance of PMP Certification

Obtaining the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is a significant milestone in a project manager’s career. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of PMP certification, and the benefits it brings, and offer tips for those considering this credential.
Understanding the Project Management Professional (PMP) Certification
The PMP certification is a globally recognized credential awarded by the Project Management Institute (PMI).
Link : https://www.pmi.org/certifications/project-management-pmp
Let’s delve into the basics of PMP eligibility:
To become a certified Project Management Professional (PMP) candidates need to fulfill requirements regarding their education and professional experience. These criteria ensure that PMP-certified professionals possess the knowledge and skills to excel in project management.
Education Requirements: Candidates must have at a high school diploma or an equivalent international qualification. This educational prerequisite establishes a level of education, for PMP certification.
Professional Experience: Alongside the requirement, candidates must demonstrate experience in project management. The specific experience criteria depend on the candidate’s background;
- For candidates with a four-year bachelor’s degree or its equivalent a minimum of three years (or 36 months) of project management experience is mandatory.
- For candidates without a four-year degree, they need to have five years (or 60 months) of project management experience.
- Project Management Education: In addition, to experience candidates are also expected to complete project management education.
Requirements for Becoming a Certified Project Management Professional
Formal Project Management Training: To become a certified Project Management Professional (PMP) you will need to complete 35 contact hours of project management training. This training can be obtained through options such as courses, workshops, or e-learning programs offered by Registered Education Providers (R.E.P.s) or accredited institutions.
Application and Examination: Once you meet the experience requirements you can proceed with submitting your PMP certification application to the Project Management Institute (PMI). After the application is approved you will have the opportunity to schedule and take the PMP certification examination. This exam evaluates your knowledge of project management principles, processes, and best practices.
Continuing Education: After achieving your PMP certification it is essential to engage in development to maintain your credentials. This involves earning many Professional Development Units (PDUs) through project management education and relevant activities.
Meeting PMP Eligibility Criteria: Meeting the eligibility criteria for obtaining a PMP certification is the step toward becoming a certified Project Management Professional. These prerequisites are designed to ensure that individuals with PMP certification possess a background of significant project management experience and demonstrate a commitment, to continuous learning. Ultimately this equips them with the skills needed to excel in managing projects and leading successful teams.
Benefits of Obtaining PMP Certification
Enhance Your Career Prospects and Open Doors, to New Opportunities
Having a PMP certification can provide you with an edge in today’s job market. It not only increases your chances of securing job offers but also opens doors to more promotions and opportunities for career growth. Employers highly value the expertise and credibility that project managers with PMP certification bring to their organizations.
Become a certified Project Manager
By obtaining your PMP certification you position yourself as a certified project manager within your industry. This prestigious credential demonstrates your commitment to excellence in project management. Showcases your ability to successfully lead projects from initiation to completion.
Gain In-Depth Knowledge and Skills
Through the process of earning your PMP certification, you will acquire knowledge and skills that are essential for effective project management. You will learn practices, proven methodologies, and strategies that can be applied across industries.
Expand Your Professional Network
With a PMP certification, you become part of a community of project management professionals. This opens up opportunities for networking with individuals who share similar goals and challenges. Building connections within this network can offer insights, mentorship, and collaboration possibilities.
Boost Confidence in Your Abilities
Achieving a PMP certification instills confidence in your abilities as a project manager. It validates your expertise. Enhances your reputation among colleagues, clients, and stakeholders
Tips for Preparing and Passing the PMP Exam
Here are some tips to prepare for the PMP exam: Recommended Books: Consider using study guides such as “PMP Exam Prep” by Rita Mulcahy or “A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide)” by PMI.
- Practice Exams: Use PMP practice exams from reliable sources like PMI’s official practice test or other reputable online platforms. Study Groups: Join PMP study groups or forums to discuss concepts, share insights, and learn from others’ experiences.
- Mobile Apps: Download PMP exam preparation apps that offer flashcards, quizzes, and study materials for on-the-go learning.
- Online Resources: Explore online forums, blogs, and YouTube channels dedicated to PMP exam tips and resources.
- Exam Strategies: Create a Study Plan: Develop a detailed study schedule that covers all PMP exam domains and allows for consistent progress.
- Time Management: Practice time management skills by allocating specific time blocks for studying and adhering to them.
- Mock Exams: Take full-length mock exams to simulate the actual testing environment and assess your readiness.
- Note-Taking: Make concise notes while studying to summarize key concepts, formulas, and processes.
- Practice Questions: Solve a variety of PMP practice questions to become familiar with question types and improve problem-solving skills.
- Revision: Regularly review previously studied material to reinforce your understanding.
- Test-Taking Tips: Question Types: Familiarize yourself with different question types, including multiple-choice, situational, and formula-based questions.
- Process of Elimination: Use the process of elimination to narrow down answer choices and increase your chances of selecting the correct option.
- Manage Anxiety: Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, to manage test-related anxiety and maintain focus.
- Stay Calm: If you encounter challenging questions, stay calm and move on to easier ones. You can revisit challenging questions later.
- Time Management: Keep track of the time during the exam to ensure you have adequate time for each section.
- Review Your Work: If time permits, review your answers to check for any errors.
Project manager tools and resources
Project managers rely on various tools and resources to effectively plan, execute, and monitor their projects. This section will explore the essential tools, organizations, and communities that can aid project managers in their roles.
Project management software and tools play a role, in helping project managers streamline their workflows and ensure the success of their projects. Here are some noteworthy options:
1. Microsoft Project: Renowned for its planning and scheduling capabilities Microsoft Project is an all-project management software. It empowers users to create project plans allocate resources effectively and track progress efficiently. This software is particularly beneficial for large-scale projects in industries such as construction and engineering.
2. Trello: Trello is a visual project management tool that employs boards, lists, and cards to organize tasks seamlessly. It caters well to sized projects while offering flexibility that suits various teams across different industries.
3. Asana: A versatile project management platform, Asana simplifies task management, project tracking, and collaboration processes. Its customizable features combined with a user interface make it an excellent choice for projects of sizes across diverse industries.
4. Jira: among software development teams Jira excels in advanced issue tracking and agile project management capabilities. It seamlessly integrates with development tools like Git and making it an ideal choice, for teams following methodologies.
Collaboration Tools:
Slack: Slack is a real-time messaging platform that enhances team communication and collaboration. It facilitates group chats, file sharing, and integration with various apps and services, making it valuable for remote and distributed teams.
Mircosoft teams: Microsoft Teams is a collaboration platform included in the Microsoft 365 suite. It brings together group chats, file sharing, and integration, with apps and services making it highly valuable for teams working remotely or across locations.
Zoom : When it comes to Zoom most people associate it with video conferencing capabilities. However, Zoom also offers features like screen sharing, webinars, and the ability to record meetings. This versatility makes it particularly useful for teams and virtual client meetings.
To-do List: For task management purposes there are a couple of apps to consider. Todo list stands out as a choice due to its simplicity and user interface. It enables users to create tasks set deadlines and organize their tasks into projects. It’s an option for individuals as well as small teams.
Wrike: Another noteworthy task management platform is Wrike. Its versatility shines through in its ability to handle both task management and project planning needs. With features such as task assignment, timelines, and resource allocation capabilities Wrike proves suitable for medium to scale projects.
Now let’s delve into the significance of Gantt charts and timelines in project management processes. These visual representations of project schedules offer assistance when planning, tracking progress, and communicating timelines effectively. By utilizing Gantt charts or timeline software solutions project managers gain insights, into task dependency paths that may impact project success or delay milestones.
Gantt charts and Timelines
Gantt charts and timeline software are essential visual tools that provide project schedules in a graphical format, making it easier to plan, track, and communicate project timelines. They are particularly useful for project managers and teams in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and event planning, where project timelines are complex and require precise coordination. These visual tools help teams understand task dependencies, critical paths, and milestones, and prevent bottlenecks, delays, and resource conflicts.
In conclusion, the utilization of tools such as Gantt charts, timeline software, collaboration platforms, and task management apps greatly benefits industries like construction, manufacturing, and event planning. The use of these resources enables communication and improved organization. Ultimately leads to more successful outcomes, for projects.
Recommended Books:
The Art of Project Management”, by Scott Berkun explores the intricacies of project management combining both art and science. The book offers insights into project planning, execution, and team dynamics. Drawing from his experience Berkun provides advice that is useful for project managers.
In “Scrum; The Art of Doing Twice the Work in Half the Time ” Jeff Sutherland, one of Scrum’s creators shares the principles and practices of this framework. This book delves into how Scrum can improve productivity and efficiency in project management.
For those seeking resources on project management, “A Girls Guide to Project Management” by Elizabeth Harrin is a blog offering a wealth of articles, templates, and tips. It caters to both novice and experienced project managers by addressing aspects of the field.
Another valuable resource is the ProjectManager.com Blog which covers a range of topics related to project management. From practices to industry trends this blog provides advice while showcasing the latest tools and techniques available.
Additionally, ProjectManagement.com serves as a community and resource hub specifically designed for project managers. It offers discussion forums, webinars, articles, and templates. Everything you need for networking purposes or seeking advice while staying updated on industry developments.
Join the project management community on Reddit; Here project managers gather to share their experiences ask questions and engage, in discussions. It’s a space where professionals can exchange insights and seek guidance.
Podcasts and Webinars
Dive into “The Project Management Podcast” by Cornelius Fichtner. This podcast features interviews with project management experts covering a range of topics. It offers a way to learn from industry leaders while on the go.
Additionally, explore PMI Webinars provided by the Project Management Institute (PMI). These webinars offer insights and timely updates on industry trends and best practices.
To expand your knowledge, skills and understanding of trends and best practices, in the field of project management we recommend delving into recommended books, blogs, online communities, podcasts and webinars.
FAQs
- What is a Project Manager?
- Response: A Project Manager is a professional responsible for planning, executing, and overseeing projects. They ensure that projects are completed on time, within scope, and within budget.
- What are the Responsibilities of a Project Manager?
- Response: Project Managers are responsible for defining project goals, managing resources, creating project plans, monitoring progress, and ensuring successful project outcomes.
- How to Become a Project Manager?
- Response: To become a Project Manager, you typically need a combination of education, experience, and certifications. Start by earning a bachelor’s degree, gain experience in project management, and consider obtaining certifications like PMP (Project Management Professional).
- What Skills are Required for a Project Manager?
- Response: Essential skills for a Project Manager include communication, leadership, time management, problem-solving, and adaptability. Technical skills and industry-specific knowledge are also valuable.
- What is the Average Salary of a Project Manager?
- Response: Project Manager salaries vary by location, experience, and industry. On average, Project Managers in the United States earn around $95,000 per year, but this can be higher or lower based on factors mentioned.
- What are Project Management Methodologies?
- Response: Project management methodologies are structured approaches to managing projects. Popular methodologies include Agile, Scrum, Waterfall, and PRINCE2, each with its own principles and practices.
- What is Agile Project Management?
- Response: Agile Project Management is an iterative approach that emphasizes flexibility and collaboration. It is well-suited for fast-changing projects and is often used in software development.
- What is the Difference Between a Project Manager and a Program Manager?
- Response: A Project Manager oversees individual projects, while a Program Manager manages a group of related projects, known as a program. Program Managers focus on strategic alignment and coordination across projects.
- What Tools Do Project Managers Use?
- Response: Project Managers use various tools, including project management software like Microsoft Project, collaboration tools like Trello or Asana, Gantt charts, and communication platforms such as Slack or Microsoft Teams.
- What are the Challenges Faced by Project Managers?
- Response: Project Managers often face challenges such as scope changes, resource constraints, schedule pressures, and team dynamics. Effective communication and problem-solving are key to overcoming these challenges.





