Introduction
In an era where the health of our planet has become the centrepiece of global conversations, the pursuit of a career that harmonizes with the rhythms of the earth is not just admirable—it’s imperative. “Sustainable Futures: Explore Environment and Sustainability jobs” is your compass to navigate the thriving landscape of green careers.
Whether you’re a budding environmentalist or a seasoned professional aiming to pivot towards a more meaningful vocation, this article illuminates the pathways that lead to impactful, fulfilling careers. Here, we delve into the heart of sustainability, unearthing the vibrant sectors, innovative roles, and dynamic opportunities that await in the realm of environment and sustainability. Get ready to embark on a journey that aligns your professional aspirations with the pressing needs of our planet, crafting a future where your career doesn’t just thrive, but also contributes to the flourishing of the Earth.

- Emerging Trends in Sustainability
- 1. Renewable Energy Revolution
- 2. Sustainable Agriculture Takes Root
- 3. Green Urban Planning: Cities of the Future
- 4. The Circular Economy in Action
- 5. Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Restoration
- 6. Water Conservation and Management
- 7. Sustainable Fashion: A Stylish Statement
- 8. Eco-Tourism: Travel with a Purpose
- Education and Skill Requirements for a Career in Sustainability
- Job Roles and Career Paths in Sustainability
- The Role of Technology and Innovation in Sustainability
- Future Outlook for Careers in Sustainability
- Top 10 FAQs
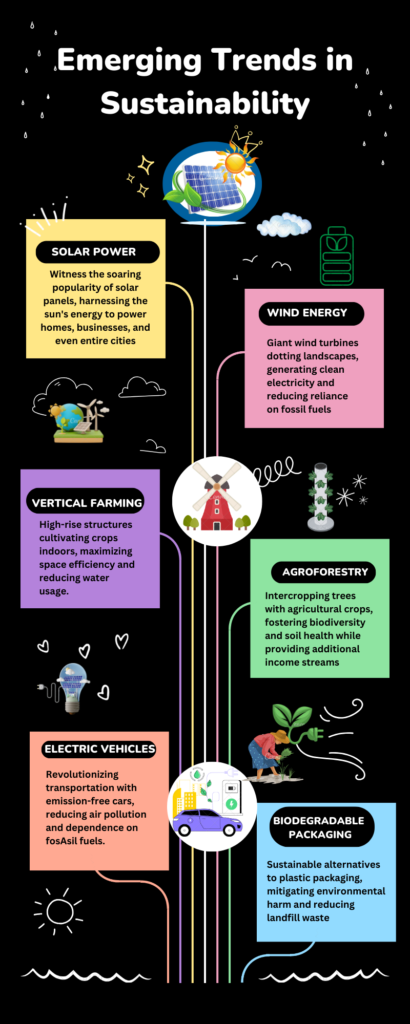
Emerging Trends in Sustainability
The sustainability field is rapidly evolving, embracing innovative technologies and practices to meet the growing demands of a world striving for balance and renewal. Here, we spotlight the most significant emerging trends, each paving the way for a greener tomorrow.
1. Renewable Energy Revolution
- Solar and Wind Power: Dominating the clean energy landscape, solar and wind technologies are becoming more affordable and efficient, driving a global shift towards these renewable sources.
- Energy Storage Breakthroughs: Advancements in battery technology, like lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, are solving intermittency issues, ensuring a steady supply of green energy.
2. Sustainable Agriculture Takes Root
- Precision Farming: Utilizing data-driven insights, farmers are optimizing resource use, ensuring that every drop of water and ounce of fertilizer counts.
- Aquaponics & Hydroponics: These soil-less farming methods are redefining urban agriculture, enabling city dwellers to grow food sustainably.
3. Green Urban Planning: Cities of the Future
- Eco-friendly Infrastructure: Incorporating green roofs, urban gardens, and permeable pavements to combat urban heat islands and enhance city livability.
- Smart City Solutions: Leveraging IoT and AI to manage resources efficiently, from smart grids managing energy use to intelligent transport systems reducing emissions.
4. The Circular Economy in Action
- Zero-Waste Initiatives: Companies are rethinking product lifecycles, designing goods that can be fully reused, repaired, or recycled.
- Sustainable Packaging: A shift towards biodegradable and compostable packaging materials is reducing the environmental footprint of consumer goods.
5. Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Restoration
- Wildlife Corridors: Establishing green bridges and corridors to promote species migration and genetic diversity.
- Reforestation Efforts: Massive tree-planting initiatives are not just combating deforestation but also restoring ecological balance.
6. Water Conservation and Management
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Technologies that adjust watering schedules based on weather forecasts and soil moisture levels to reduce water wastage.
- Water Recycling: Advanced treatment technologies turning wastewater into a resource for various non-potable uses.
7. Sustainable Fashion: A Stylish Statement
- Eco-Fabrics and Dyes: The rise of organic and recycled materials is transforming the fashion industry, making sustainability the new trend.
- Ethical Supply Chains: Transparency in sourcing and fair labor practices are becoming pivotal in consumer choices.
8. Eco-Tourism: Travel with a Purpose
- Conservation Holidays: Vacations that contribute to the preservation of wildlife and support local communities.
- Green Accommodations: Hotels and resorts adopting sustainable practices, from energy efficiency to reducing plastic use.
In conclusion, these emerging trends in sustainability demonstrate a collective move towards a future where technology, innovation, and conscientious practices unite to forge an environmentally sound and prosperous world. As these trends evolve, they promise not just to reshape our environmental landscape but also to offer myriad opportunities for those seeking careers in the burgeoning field of sustainability.

Education and Skill Requirements for a Career in Sustainability
Embarking on a career in sustainability demands a fusion of specialized education and versatile skills. Below, we outline the educational paths and skill sets that form the bedrock of success in this dynamic field.
Educational Backgrounds
A strong educational foundation is pivotal. Here’s how different degrees can catapult you into the sustainability sector:
| Degree Type | Relevance |
|---|---|
| Environmental Science | Delve into ecosystem dynamics, conservation practices, and environmental restoration. |
| Engineering (Environmental, Chemical, Mechanical) | Innovate and develop sustainable technologies, green infrastructure, and energy solutions. |
| Environmental Policy & Law | Shape policies, ensure legal compliance, and advocate for environmental justice and sustainable practices. |
| Business & Sustainability | Merge commercial acumen with sustainability principles to drive eco-friendly business models. |
| Urban Planning | Design sustainable, livable, and resilient urban spaces, integrating green spaces and infrastructure. |
Necessary Abilities
Alongside a degree, a diverse range of skills can make you stand out.
Technical Competence
Grasp the aspects of sustainability. Be proficient, in using tools and technology that drive sustainable practices.
Project Management
Efficiently collaborate on projects, managing time, resources and team dynamics to achieve sustainability goals.
Critical Thinking:
Analyze and resolve problems by making well informed decisions that balance ecological, economic and social factors.
Innovative Mindset:
Stay ahead of the game by embracing technologies and approaches that push the boundaries of sustainability.
Communication:
Articulate concepts related to sustainability to audiences in a persuasive manner promoting awareness and inspiring action.
Adaptability:
Navigate through the changing landscape of sustainability adapting to challenges and opportunities with resilience and foresight.
Networking
Establish connections with professional’s organizations and communities to exchange knowledge collaborate on initiatives. Build a support system.
Ethical Judgment
Ethical standards to ensure that sustainability efforts are genuine, transparent and socially responsible.
In conclusion combining a foundation with a diverse range of skills opens doors for a successful career, in sustainability.
As the field continues to evolve being adaptable well informed and connected becomes crucial.
Whether you’re a student mapping out your path or a professional aiming to create an impact these guidelines act as your guide, in the changing and optimistic realm of sustainability.
Job Roles and Career Paths in Sustainability
The realm of sustainability offers a range of job opportunities and career paths all of which play a role, in shaping a more environmentally aware and resilient world. Here’s an overview of some job titles and the paths they entail:
- Sustainability Coordinator
Creating and implementing sustainability initiatives within organizations monitoring progress towards sustainability goals and engaging with stakeholders.
Career Path: Entry level positions often begin as sustainability assistants or interns leading to coordinator roles as experience is gained. - Environmental Engineer
Designing, developing and implementing solutions to challenges such as pollution control systems and waste management strategies.
Career Path: Entry level positions usually require a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a related field with opportunities for advancement to engineering roles. - Policy Analyst
Roles: Analysing policies and regulations offering recommendations for policy development and advocating for practices.
Career Path: Typically requires a background in policy, public policy or a related field. There are opportunities for growth into analyst or policy advisor roles. - Conservation Scientist
Conducting research, on ecosystems and wildlife creating conservation plans and collaborating with stakeholders to safeguard habitats. Career Path: Starting out in the energy field you can begin as a research assistant or a field technician. As you gain experience you can progress to roles, like scientist or project manager. - Renewable Energy Specialist
Your role would involve designing, installing and maintaining energy systems such as panels and wind turbines. Additionally, you would provide advice on energy efficiency measures.
Career Path: You could start as a technician or an installer and then have the opportunity to advance to becoming a specialist or a project manager. - Sustainability Consultant
Responsibilities; As a sustainability consultant your expertise would be sought by organizations looking for guidance on practices. You would conduct sustainability assessments. Develop strategies for improvement.
Career Path: You may begin as a consultant or analyst and work your way up to becoming a consultant or taking on project lead roles. - Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Manager
Responsibilities: In this role you would be responsible for developing and implementing CSR strategies within an organization. Your tasks would include engaging with stakeholders and monitoring the company’s sustainability performance.
Career Path: Entry level positions often start in CSR or sustainability departments but there are opportunities for advancement, into directorial roles.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in Sustainability
Technological advancements have brought about a transformation, in the field of sustainability opening up career prospects across various sectors. Lets explore how technology and innovation are driving progress in sustainability;
- Green Technology: The introduction of technologies is revolutionizing industries by minimizing environmental impact and enhancing resource efficiency. For instance, smart grids are being used for energy management electric vehicles are transforming transportation and sustainable building materials are being utilized in construction projects.
- Clean Energy Solutions: Breakthroughs in clean energy technologies are reshaping the energy sector. Creating job opportunities. Solar power, wind energy and hydropower have become more cost effective and accessible than before leading to an increased demand for professionals in renewable energy production and distribution.
- Product Design: Technological advancements enable the development of eco products and materials that promote sustainable consumption and production practices. From packaging to energy appliances careers in research, development and manufacturing of sustainable products offer exciting prospects.
- Data Analytics and Monitoring: Organizations now have access to data analytics tools that empower them to track their performance effectively. Sustainability professionals utilize these tools to assess energy usage monitor emissions identify areas for improvement; this creates opportunities in data analysis as environmental consulting.
- Circular Economy Solutions: Technology plays a role in facilitating the transition towards an economy where resources are reused, recycled or repurposed instead of being discarded.
These advancements demonstrate how technology is driving progress, towards a future while simultaneously providing individuals with promising career paths. Careers, in the field of environment and sustainability solutions involve tasks such as designing systems that operate in a closed loop manner developing technologies for recycling and implementing practices for managing waste.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has brought about a revolution in the realm of sustainability by enabling real time monitoring and control of systems.
Some examples of applications include precision farming for agriculture, water management systems that promote conservation and energy efficient smart buildings. These advancements offer career opportunities in the development and implementation of technology.
To summarize, technology and innovation play a role in driving sustainability. They provide career paths in areas such as tech, clean energy, sustainable product design, data analytics, circular economy solutions and IoT applications. As technology continues to progress so will the chances to make impacts, through innovative solutions and sustainable practices.
Home | Padcare Labs is one such organization who are recycling sanitary pads. They have a complete ecosystem set-up to recycle sanitary pads thus saving the environment.
Check out this video to learn about the recycling journey.
Future Outlook for Careers in Sustainability
The future of sustainability careers looks bright as we anticipate growth and innovation, in response to environmental trends. Lets take a look at what lies
Increasing Demand for Sustainability Professionals; As businesses and governments place greater emphasis on sustainability we can expect a higher demand for professionals skilled in environmental conservation renewable energy and sustainable development.
Expanding Opportunities in Fashion: With consumers becoming more aware of ethical concerns within the fashion industry there is a growing need for experts in sustainable fashion design, production and marketing.
Emerging Prospects in the Circular Economy: The transition towards an economy that promotes resource reuse and recycling is opening up avenues in waste management recycling technology and sustainable supply chain management.
Development of Green Infrastructure: The push for infrastructure encompassing energy projects, green buildings and eco friendly transportation systems is fuelling career opportunities in urban planning, civil engineering and sustainable construction.
Innovations in Clean Energy: Technological advancements in energy sources like wind power are expected to create fresh job prospects, within renewable energy production, energy storage solutions and modernizing power grids.
The role of sustainability consultants is expanding as businesses aim to enhance their performance and achieve sustainability objectives. This trend is expected to create opportunities, for professionals who specialize in sustainability strategy and implementation.
There is a growing demand for experts in climate adaptation, disaster resilience and natural resource management due to the impact of climate change and other environmental challenges.
To sum up careers in sustainability have a future. There will be growth prospects in fields, like fashion, circular economy, green infrastructure, clean energy, sustainability consulting and addressing environmental challenges. As our world moves towards a path professionals will have increasing chances to make positive contributions and promote environmental stewardship.
If you wish to explore other career options, visit our blog
Top 10 FAQs
- What kind of jobs are available in the environment and sustainability field?
There’s a vast array! From conservation scientists and policy analysts to renewable energy engineers and sustainable product designers, opportunities span various sectors like government, non-profits, research institutions, and private companies.
- What qualifications do I need to get an environment and sustainability job?
Educational requirements vary depending on the specific role. Many positions require bachelor’s degrees in environmental science, ecology, engineering, policy, or related fields. Relevant certifications, internships, and volunteer experience can significantly boost your candidacy.
- What skills are essential for these jobs?
Strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills are crucial. Additionally, proficiency in data analysis, GIS mapping, and sustainability principles is often advantageous.
- Do I need a science background to work in sustainability?
Not necessarily! While science backgrounds are valuable, other disciplines like law, business, communication, and social sciences also contribute significantly to sustainability efforts.
- What are the salary ranges for these jobs?
Salaries vary based on experience, location, specific role, and employer. However, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects above-average job growth and earning potential for many green jobs in the coming years.
- Where can I find environment and sustainability jobs?
Look for postings on environmental job boards, company websites, government agency websites, and professional networking platforms like LinkedIn. Additionally, attending sustainability conferences and events can connect you with potential employers.
- How can I break into the field if I have no experience?
Start by gaining relevant skills through internships, volunteer work, or online courses. Networking with professionals in the field and attending industry events can provide valuable insights and connections.
- What are the biggest challenges in the environment and sustainability field?
Climate change, biodiversity loss, and resource depletion pose significant challenges. However, these challenges also create opportunities for innovation and problem-solving in various sectors.
- What are the ethical considerations in these jobs?
Sustainability often involves complex social, economic, and environmental factors. Ensuring ethical practices and considering diverse perspectives are crucial considerations in this field.
- What can I do to make a real difference in this field?
The most impactful contribution depends on your skills and interests. Consider research, policy advocacy, education, community engagement, or business innovation – every role plays a part in creating a more sustainable future.





