Introduction

Are you someone who enjoys technology, innovation, and bringing together teams from different fields to create game-changing products? If that’s what you’re looking for, a career as a Product Manager may be just right for you. Shaping and delivering successful products to the market is a crucial responsibility of Product Managers. This guide will delve into the exciting realm of product management, covering key responsibilities, essential tools like Jira and Primavera6, product planning, and the significance of Product Management Monday. When you reach the end of this article, you’ll have a deeper insight into what it means to be an exceptional Product Manager.
Define Project Management
The process of product management includes identifying customer needs, validating solutions, and delivering value through products. Product managers serve as the link between the market and the development team. Product management is a fascinating and fulfilling career that demands a diverse skill set, including technical, business, and interpersonal skills. The primary responsibility of a product manager is to comprehend customers’ problems, goals, and preferences to transform them into product requirements. They also have to prioritize the most crucial features, align the team around a common vision, and ensure that the product meets the quality standards and user expectations.
Product management is a challenging but satisfying career path that offers ample opportunities for personal and professional growth. The career demands a combination of technical expertise, business acumen, and exceptional communication skills to succeed. The role also offers plenty of opportunities to learn, evolve, and make a meaningful impact on the world.
Who is a Product Manager?
A Product Manager is a professional who plays a role in the development, release and ongoing success of a product or service. They act as a connector between parties involved, including customers, engineering teams, marketing and sales. Their main objective is to ensure that the product aligns with the company’s goals and meets customer needs.
Product Managers are accountable for defining the vision of the product, devising a strategy, and executing it to deliver a product that resonates with the intended audience. Essentially, they take on the role of being the “CEO” of the product by overseeing its lifecycle from start to finish.In order to succeed in their role Product Managers must be adaptable to changing customer needs, market trends, competitor actions and user feedback. Additionally, they must effectively balance the requirements of stakeholders such as executives, investors, partners and regulators.
Role of a Product Manager
As a Product Manager, your responsibilities encompass a wide range of activities. Here are some of the key aspects of the role:
a. Product Strategy
As a Product Manager, one of your key responsibilities is to develop and communicate a clear product vision that outlines where you want to take the product and how it will deliver value to customers. This involves:
- Defining the product vision: You need to have a clear understanding of what the product is and what it will do for customers. This involves identifying the product’s unique selling proposition, its core functionalities, and its potential for growth.
- Setting strategic goals and objectives: Once you have a clear product vision, you need to set strategic goals and objectives that align with the company’s overall business strategy. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time bound.
- Identifying market opportunities and threats: To develop a successful product, you need to have a deep understanding of the market and its dynamics. This involves conducting market research to identify customer needs, pain points, and preferences, as well as analyzing competitor offerings and market trends.
- Defining the product’s purpose: You need to define the product’s purpose, target audience, and value proposition based on your market research. This involves identifying the customer segments that the product will serve, their needs and preferences, and how your product addresses those needs better than the competition. You should also identify the key features and benefits that differentiate your product from others in the market.
b. Market Research and Analysis
To successfully navigate a career as a Product Manager, it’s essential to have a strong grasp of market research and analysis. Some key aspects of this include:
- Conducting thorough market research to gain a deeper understanding of customer needs, wants, and pain points. This research can take many forms, from surveys and focus groups to in-depth interviews and data analysis.
- Gathering and analyzing data to make informed decisions. This includes both internal data (such as user engagement metrics) and external data (such as industry trends and competitor insights). Product Managers should be comfortable working with data and using it to drive decision-making.
- Researching and studying the competitive landscape and market trends. This includes monitoring competitors’ product offerings, pricing strategies, and marketing tactics, as well as keeping up-to-date with broader industry trends and developments. By staying informed about what’s happening in the market, Product Managers can make smarter decisions about product development and positioning.
c. Roadmapping
As a Product Manager, you play a crucial role in developing and executing a product roadmap that outlines the product’s development over time. To do this effectively, you need to:
- Prioritize features and enhancements based on customer feedback and business objectives. This means understanding the needs of your customers and the goals of your business, and aligning your product development strategy accordingly.
- Plan the product’s development timeline and feature releases. This includes setting deadlines, identifying dependencies, and allocating resources to ensure that the product is delivered on time and within budget.
- Continuously monitor and adjust the roadmap based on feedback and changing market conditions. This means being flexible and adaptable, and being willing to pivot when necessary to keep the product on track.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your product development efforts are focused, effective, and aligned with the needs of your customers and your business.
d. Cross-functional Collaboration
As a Product Manager, you will need to collaborate with multiple teams to ensure that the product is developed and launched successfully. To do this effectively, you should:
- Collaborate with engineering, design, marketing, and sales teams to ensure alignment. This means working closely with each team to understand their needs and priorities, and ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goals.
- Communicate the product’s vision and requirements effectively. This involves clearly articulating the product’s purpose, target audience, and value proposition, as well as its key features and functionality. You should be able to communicate the product’s vision in a way that inspires your team and motivates them to work towards achieving the product’s goals.
- Utilize tools like Jira or Primavera P6 to manage tasks, track progress, and facilitate communication across teams. This means using project management tools to keep everyone on the same page, and to ensure that tasks are performed on time and to a high standard. You should be able to use these tools to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to keep the project moving forward.
e. Product Development
As a Product Manager, your role encompasses overseeing the entire product development process from inception to launch. Here are the key aspects of this responsibility:
- Monitoring progress: You need to keep a close eye on the development process and ensure that everything is on track. If any issues arise or things aren’t progressing as planned, you need to identify the problem and make adjustments as needed.
- Defining functionalities and workflows: You’ll be responsible for defining the product’s functionalities and workflows. Your goal is to ensure that the product is easy to use and provides a seamless experience for the users.
- Articulating the product vision: You need to be able to clearly communicate the product vision to stakeholders, including executives, investors, and the development team. You’ll need to articulate how the product aligns with the company’s goals and how it will provide value to the target audience.
- Pitching ideas: You’ll be responsible for pitching new ideas to stakeholders and getting their buy-in. This will require strong communication skills and the ability to clearly articulate the benefits of the idea.
- Communicating progress: Throughout the development process, you’ll need to keep stakeholders informed about progress and any changes. This will require effective communication skills and the ability to provide updates in a clear and concise manner.
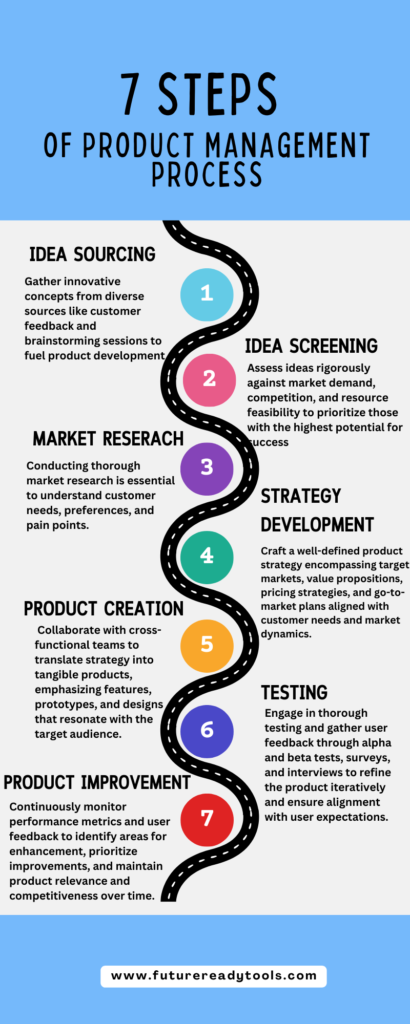
f. Launch and Meeting
As a Product Manager, planning and executing product launches as well as coordinating marketing efforts to promote the product are key responsibilities. Here are some ways you can achieve success in these areas:
- Develop a Launch Plan: A well-thought-out launch plan is crucial to the success of any new product. This should include a timeline of key activities, messaging and positioning, target audience, and the channels you’ll use to reach them.
- Coordinate with Cross-functional Teams: Coordination with cross-functional teams, including engineering, design, marketing, and sales, is essential to ensure a smooth and successful launch. Make sure everyone is aware of their roles and responsibilities, and communicate regularly to stay on track.
- Create Marketing Collateral: Develop marketing collateral that aligns with the product’s messaging and positioning. This may include website content, product demos, social media posts, email campaigns, and other promotional materials.
- Develop a Sales Strategy: Work with the sales team to develop a sales strategy that aligns with the product’s value proposition and target audience. This may include identifying key accounts, developing sales scripts, and conducting training sessions.
- Monitor Launch Performance: Keep a close eye on launch performance using metrics and analytics. Identify areas for improvement, adjust your strategy if needed, and continue to iterate based on data insights.
- Coordinate Post-launch Activities: Once the product is launched, coordinate post-launch activities such as customer feedback collection, bug tracking, and ongoing marketing efforts. Continuously monitor and adjust your strategy to ensure ongoing success.
g. Performance Monitoring
As a Product Manager, it’s important to track your product’s performance, make data-driven decisions, and iterate based on data insights. Here are some ways to achieve success in these areas:
- Use Metrics and Analytics: Use metrics and analytics to track your product’s performance. This may include user engagement, retention rates, conversion rates, and other key performance indicators (KPIs). Use this data to identify areas for improvement.
- Make Data-Driven Decisions: Use the data you collect to make informed decisions about how to optimize your product. Don’t rely on assumptions or hunches – let the data guide your decisions.
- Measure Product Performance: Continuously measure your product’s performance to identify areas for improvement. Use the data you collect to iterate and optimize your product.
Key Skills and Qualities of a Successful Product Manager
As a Product Manager, your role is critical in the development, launch, and success of a product or service. To excel in this role, yoau need to possess a diverse range of skills and qualities.
Communication:
Effective communication is a crucial skill for Product Managers. You will need to convey the product vision and requirements to various teams, as well as communicate with stakeholders at all levels of the organization.
Leadership:
Leadership skills are also essential for guiding cross-functional teams and making tough decisions. You will need to inspire and motivate team members towards a common goal, provide direction, and ensure that everyone is working towards the same objectives.
Analytical Thinking:
Analytical thinking is another key skill for Product Managers. You will need to analyze data, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. This involves working with data to inform your decisions, such as customer feedback, market research, and performance metrics.
Problem Solving:
Problem-solving is another critical skill for Product Managers. You will face complex challenges and must devise innovative solutions to overcome them. You must be able to think outside the box and come up with creative solutions to ensure the product’s success.
Adaptability:
Adaptability is crucial in the tech industry, which evolves rapidly. As a Product Manager, you must be able to adapt to changing market trends, customer needs, and new technologies. This means being flexible and open to change, and always willing to learn.
Empathy:
Empathy is also essential for Product Managers, as you need to understand customer needs and pain points to create products that resonate with users. You must be able to put yourself in the shoes of your customers to create products that meet their needs and exceed their expectations.
Technical Knowledge:
Having technical knowledge can be beneficial in working with development teams. As a Product Manager, you must understand the technical aspects of your product and communicate effectively with developers to ensure that the product meets all requirements.
Insights from Product Managers Using Jira and Primavera P6
In the world of product management, the choice of tools can greatly impact productivity and efficiency. Two popular tools frequently used by Product Managers are Jira and Primavera6.

a. JIRA
Jira is a popular project management and issue-tracking tool . Product Managers often rely on Jira to create and manage tasks, track progress, and collaborate with development teams. Here are some key features of Jira that make it a valuable tool for Product Managers:
1. Agile Project Management: Jira allows for agile project management, which means that it is easy to adapt to changing requirements and priorities. This is particularly useful for Product Managers who need to be able to pivot quickly based on customer feedback and market trends.
2. Task Management: Jira allows Product Managers to create and manage tasks easily. Tasks can be assigned to team members, given due dates, and prioritized according to importance. This helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that work is being done efficiently.
3. Collaboration: Jira makes it easy for Product Managers to collaborate with development teams. They can use the tool to communicate with team members, share files, and get feedback on tasks. This helps to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal and that there are no misunderstandings.
4. Integration: Jira integrates with a variety of other tools, which enhances its versatility and functionality. For example, Jira can be integrated with Confluence (Atlassian’s wiki tool) to help teams document important information and collaborate more effectively.
Overall, Jira is an essential tool for Product Managers who are looking to streamline their work and improve collaboration with their development teams. Its agile project management capabilities, task management features, and integration with other tools make it a valuable asset for any Product Manager.
b. Primavera6
- Primavera6 is a highly effective project management software that is frequently used in industries like engineering and construction.
- Product Managers can utilize Primavera6 to create comprehensive project plans and schedules in great detail.
- With advanced features for resource management, cost tracking, and risk analysis, Primavera6 is particularly useful for complex projects.
- Although it may not be as prevalent in every industry, Primavera6 can be an extremely powerful tool for Product Managers overseeing large-scale projects.
External link: Coursera
c. Art of Product Planning:
The art of product planning is a crucial phase in the product management process. It involves setting the direction, goals, and features for the product. The planning phase lays the foundation for a successful product and is, therefore, essential to get right. Effective product planning requires a deep understanding of the target audience, their needs, and the market trends. It also involves analyzing competitor products and identifying opportunities for differentiation.
Market Analysis
To ensure the success of your product, it is crucial to conduct thorough market research before diving into development. Here are some specific steps you can take to conduct effective market research:
- Define your target audience: Identify the specific demographic, psychographic, and behavioral characteristics of your ideal customer. This will help you tailor your product and marketing efforts to their needs and preferences.
- Analyze your competition: Research your competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. This will help you identify gaps in the market and opportunities for innovation.
- Conduct customer surveys: Gather feedback from potential customers to understand their pain points, needs, and preferences. This will help you validate your product idea and ensure that it aligns with customer needs.
- Evaluate pricing and distribution: Research pricing strategies and distribution channels to determine the best approach for your product. This will help you maximize profitability and reach your target audience effectively.
By following these steps and conducting thorough market research, you can ensure that your product meets the needs of your target audience and stands out in a crowded market.
Customer Feedback
To gather feedback from current customers and potential users, there are several effective strategies that Product Managers can use:
- Conduct surveys: Create surveys to gather feedback from users on their experience with the product. Questions should focus on what users like about the product, what they dislike, and what features they would like to see added or improved.
- Conduct interviews: Conduct interviews with current customers and potential users to gain deeper insights into their needs and pain points. These interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
- Use feedback channels: Set up feedback channels, such as email or social media, to allow users to share their thoughts and feedback. Respond promptly to feedback and take action to address any issues or concerns.
- Track metrics: Track metrics such as user engagement, retention, and conversion rates to gain insights into how users are interacting with the product and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze user behavior: Analyze user behavior using tools like Google Analytics or Mixpanel to gain insights into how users are using the product and identify areas for improvement.
By implementing these feedback gathering strategies, Product Managers can gain valuable insights into user needs and pain points, which can be used to improve the product and drive user engagement and satisfaction.
Prioritizing
1. Start by listing the features and enhancements that you want to prioritize based on customer feedback and business objectives.
2. By using the Eisenhower Matrix to prioritize features and enhancements, you can ensure that you are focusing on the most important items that align with your business objectives and customer needs.
Roadmapping
To develop a product roadmap that outlines the timeline for feature releases and major milestones, you should consider the following steps:
- Define the product vision and strategy: Before creating the roadmap, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the product vision, target audience, and value proposition. Identify the key features and functionalities that are critical to achieving the product’s goals.
- Map out the development timeline: Once you’ve identified the most critical features, create a timeline for their development and release. Consider the dependencies between features, the estimated time for development, and the resources needed to complete each feature.
- Align with cross-functional teams: Collaborate with engineering, design, marketing, and sales teams to ensure alignment and buy-in for the roadmap. Communicate the product vision and requirements effectively and obtain feedback and input from each team.
- Set milestones and checkpoints: Define the key milestones and checkpoints for each feature’s development, such as alpha and beta releases, user testing, and quality assurance. These milestones can serve as a guide to track progress and ensure that the product is on track.
- Iterate and adjust: As you develop the product, be open to feedback and make adjustments as needed. Track user feedback and analytics to determine if the product is meeting customer needs and adjust the roadmap accordingly.
By following these steps, you can develop a product roadmap that aligns with the product’s overall strategy and guides the development process to deliver a successful product.
MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
To build an effective MVP, consider these key points:
- Identify the essential features needed for the product to function and avoid any unnecessary additions that could slow down development.
- Keep the design user-friendly and straightforward, focusing on getting the product to early adopters as soon as possible for feedback.
- Utilize existing tools and technologies to expedite the development process, such as open-source software, cloud services, and third-party APIs.
- Test the MVP with a small group of users, gather feedback, monitor performance, iterate and refine the MVP based on data insights, and use these insights to inform your product strategy and roadmap for the full-scale launch.
The Power of Product Management Monday
Product Management Monday (PMM) is more than just a catchy phrase, it’s a methodology that propels product managers towards structured and efficient practices. By adhering to PMM principles, product managers can streamline their workflows and maximize productivity. Let’s delve into the key components of PMM and explore how they can revolutionize your approach to product management.
Weekly Planning: Setting the Stage for Success
Designate Mondays as the cornerstone of your product management activities. Use this dedicated time to reflect on the previous week’s progress, set clear goals for the upcoming week, and prioritize tasks accordingly. By starting the week with a well-defined plan, you set yourself up for success and ensure that your efforts remain focused and purposeful.
Stakeholder Communication: Building Alignment from the Start
Effective communication is the lifeblood of successful product management. Schedule meetings and interactions with cross-functional teams early in the week to ensure that all stakeholders are aligned on the product’s direction and goals. By fostering open dialogue and collaboration, you lay the foundation for a cohesive and harmonious approach to product development.
Metrics and Analytics: Guiding Decisions with Data
In today’s data-driven landscape, metrics and analytics play a pivotal role in informing decision-making. Dedicate time each week to analyze product metrics and customer feedback, using data to gain valuable insights and identify areas for improvement. By leveraging data-driven insights, you can make informed decisions that drive product success and resonate with your target audience.
Agile Principles: Embracing Adaptability and Iteration
Incorporate agile methodologies into your product management approach to adapt to changing requirements and feedback. Break down tasks into smaller, manageable units and iterate as needed, allowing for greater flexibility and responsiveness to evolving market dynamics. By embracing agility, you empower your team to navigate complexity with confidence and deliver value iteratively.
Documentation: Ensuring Clarity and Accountability
Maintaining thorough documentation of product plans, roadmaps, and decisions is essential for clarity and accountability within the team. By documenting key insights and decisions, you provide a reliable reference point for team members and stakeholders, fostering transparency and alignment. Additionally, documentation serves as a valuable tool for onboarding new team members and facilitating knowledge sharing across the organization.
Exploring Career Paths and Growth Opportunities
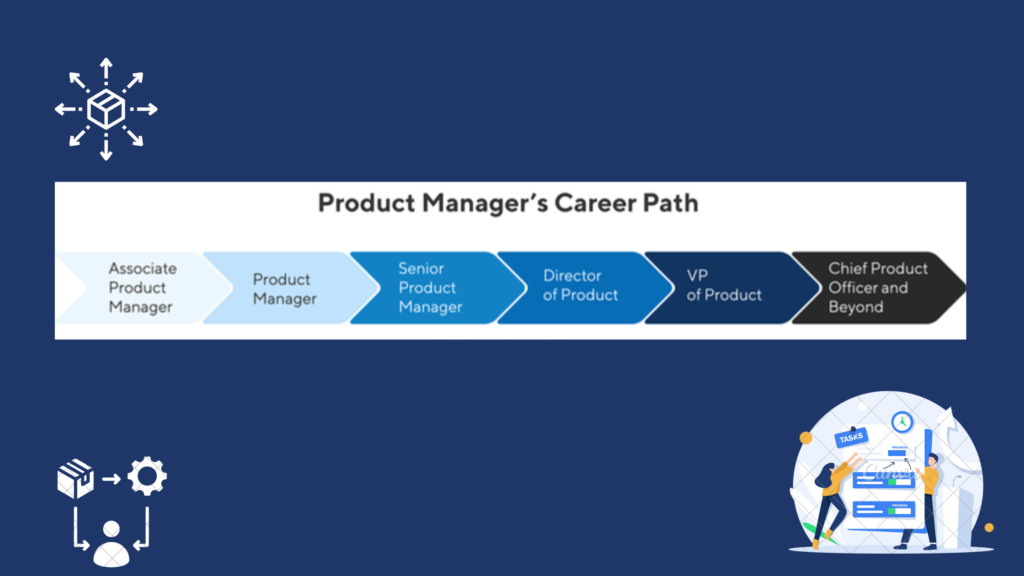
A career in product management offers a multitude of growth opportunities and diverse career paths to explore. Whether you aspire to climb the ranks within an organization or venture into entrepreneurship, the possibilities are limitless. Here are some potential paths and roles to consider:
Senior Product Manager:
As you gain experience, you can transition into roles with greater complexity and responsibility. Senior Product Managers often oversee high-impact projects and play a pivotal role in shaping the product strategy.
Director of Product Management:
This leadership role involves overseeing multiple product managers and product lines, setting the overall product strategy for the organization, and driving innovation and growth.
Chief Product Officer (CPO):
At the pinnacle of the product management hierarchy, the CPO holds the highest-ranking executive position. CPOs are instrumental in shaping the company’s product vision and portfolio, driving strategic initiatives, and fostering innovation.
Entrepreneurship:
Many successful product managers leverage their expertise to launch their ventures or join startups. The entrepreneurial mindset and strategic acumen cultivated in product management are invaluable assets for aspiring founders.
Product Management Consulting:
Share your expertise with other organizations by becoming a product management consultant. Help companies optimize their product development processes, refine their strategies, and drive business growth.
To learn more about other careers
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a career in product management is a thrilling journey filled with opportunities for innovation, leadership, and strategic impact. By embracing methodologies like Product Management Monday and leveraging essential tools and techniques, you can excel in this dynamic field. Whether you’re embarking on your first steps or seeking to advance your career, the possibilities in product management are boundless. So, seize the moment and embark on a journey that has the potential to reshape the future of technology and innovation.
FAQ’S
- What does a Product Manager do?
A. A Product Manager is a professional who plays a role, in guiding the development, strategy and overall success of a product or service. They act as a link between teams to ensure that the product aligns with the companys goals and meets customer needs.
2. What steps should one take to become a Product Manager?
A. To embark on a career as a Product Manager it typically requires a combination of education and experience. Many successful Product Managers come from backgrounds in business, engineering or design. Gaining experience in roles involving project management, leadership and cross functional collaboration is also highly valuable.
3. What are the primary duties of a Product Manager?
A. The primary responsibilities of a Product Manager encompass defining product strategy conducting market research creating roadmaps collaborating effectively with cross functional teams overseeing the entire product development process from start to finish launching new products successfully into the market and continuously monitoring their performance.
4. Which skills are essential for someone aspiring to be a Product Manager?
A. Essential skills for individuals aiming to become Product Managers include communication abilities both verbal and written; strong leadership qualities; analytical thinking capabilities; problem solving aptitude; adaptability to changing circumstances; empathy towards end users needs and desires; as well, as solid technical knowledge. Possessing these skills enables them to effectively manage products and lead teams.
5. What tools do seasoned Product Managers utilize?
A. Product Managers typically utilize a range of tools to assist in their work, which includes project management software, like Jira, product management tools such as Aha! and Trello, data analytics platforms, customer feedback systems and communication tools.
5. Could you provide information on the salary for Product Managers?
A. The salary of a Product Manager can vary depending on factors such as location, industry experience and the specific industry.
6. How do Product Managers determine feature priorities?
A. Product Managers prioritize features by considering elements including business objectives customer feedback insights gathered from market research efforts. They also employ techniques like the Eisenhower Matrix and cost benefit analysis to aid in making decisions.
7. What does Agile product management entail?
A. Agile product management is an iterative approach to developing products. It places emphasis on collaboration with stakeholders and customers while remaining flexible enough to adapt based on their input. By utilizing methodologies Product Managers are able to respond to evolving market demands and changing requirements effectively.
8. What are some challenges faced by Product Managers?
A. Product Managers encounter a range of challenges including managing conflicting priorities among stakeholders or teams involved in a project. Additionally balancing short term goals with long term objectives can often prove challenging. The ability to navigate ambiguity within projects is also crucial along with communication, across teams.
9. Are certifications important for Product Managers?
A.It’s quite common for Product Managers to face the challenge of adapting to evolving technology and market trends. Now lets dive into the topic of certifications, for Product Managers. While certifications can hold value for these professionals they aren’t always a requirement. Some individuals choose to pursue certifications such, as Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO) or Pragmatic Marketing Certification in order to enhance their skills and appeal in the job market. On the hand many rely on their experience and expertise without necessarily needing formal certification.